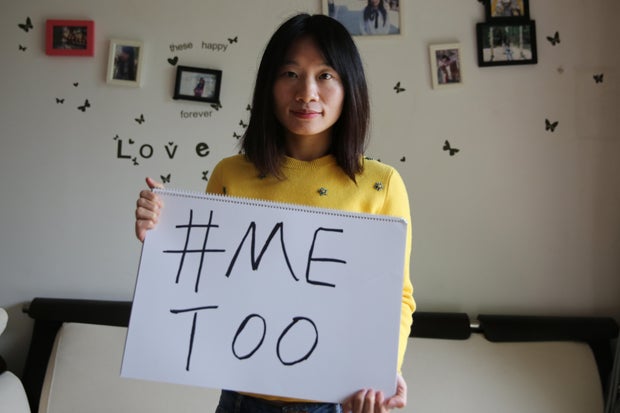Prominent #MeToo journalist and activist Sophia Huang Xueqin, 36, was convicted by a court in China of “subversion against the state” on Friday and given a five year prison sentence, according to her supporters.
Huang reported groundbreaking stories about sexual abuse victims and survivors in China, and had spoken about misogyny and sexism she faced herself in newsrooms of the state-run media. Her trial was held behind closed doors at the Guangzhou Intermediate People’s Court in southern China.
The verdict was not immediately confirmed by Chinese judicial authorities.
Thomas Yau/South China Morning Post/Getty
Huang was detained alongside labor rights activist Wang Jianbing in 2021 at an airport in Guangzhou. Their supporters say they were held in solitary confinement for months during their pre-trial detention, and that the trial only began in September 2023.
According to a Friday social media posts by the “Free Huang Xueqin & Wang Jianbing” group, the charges against Huang related to meetings she had led in Guangzhou from late 2020, during which the court ruled she had “incited participants’ dissatisfaction with Chinese state power under the pretext of discussing social issues.”
The supporters’ group said Wang was also sentenced on Friday, to three years and six months in prison, on the same charges.
When she was arrested at the airport, Huang had been on her way to start working toward a masters degree in Britain, on a U.K.-government sponsored scholarship program.
The convictions “show just how terrified the Chinese government is of the emerging wave of activists who dare to speak out to protect the rights of others,” Amnesty International’s China Director Sarah Brooks told CBS News’ partner network BBC News on Friday.
Amnesty International called the convictions “malicious and totally groundless.”
Chinese authorities launched a crackdown on activists working in different fields in 2021, BBC News reported.
“#MeToo activism has empowered survivors of sexual violence around the world, but in this case, the Chinese authorities have sought to do the exact opposite by stamping it out,” Brooks said.